Spring学习
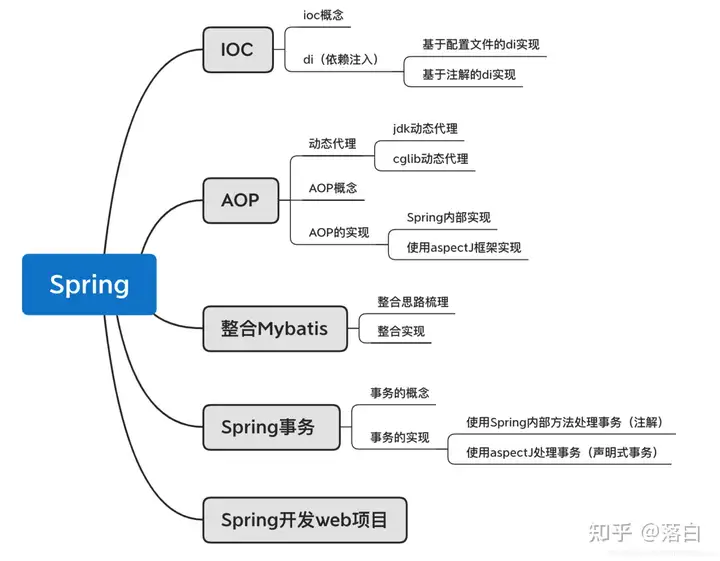
1、Spring框架体系
2、 IOC
2.1 什么是IOC
IoC (Inversion of Control) : 控制反转, 是一个理论,概念,思想。把对象的创建,赋值,管理工作都交给代码之外的容器实现, 也就是对象的创建是有其它外部资源完成,这样做实现了解耦合。
正转:对象的创建、赋值等操作交由程序员手动完成,即使用类似new Xxx(Xxx Xxx)、Xxx.setXxx()语句完成对象的创建与赋值,缺点是一旦程序功能发生改变,涉及到的类就要修改代理,耦合度高,不便于维护和管理。
反转:对象的创建、赋值等操作交由代码之外的容器实现,有容器代替程序员完成对象的创建、赋值;且当程序功能发生变化时,只需要修改容器的配置文件即可。
java实现创建对象的方式有哪些
1、构造方法:new student()
2、反射
3、序列化
4、动态代理
5、容器:tomcat容器、ioc容器
容器创建对象的场景:在tomcat服务器启动时会实例化servletContext上下文对象;在发出请求时,相应的servlet对象也不是由开发人员进行实例化的,而是在tomcat内部由tomcat容器实例化的
2.3 基于配置文件的di实现
2.3.1 什么是di
DI(Dependency Injection) :依赖注入, 只需要在程序中提供要使用的对象名称就可以, 至于对象如何在容器中创建, 赋值,查找都由容器内部实现。
DI是ioc技术的实现方式(即容器如何创建对象这一问题的实现方式)
2.3.2 入门案例
使用ioc容器创建对象,调用对象的方法
2.3.3 环境搭建
创建maven项目,目前都是javase项目,推荐使用骨架,选择quickstart
加入maven依赖:分别是spring依赖、junit依赖
创建类(接口和它的实现类)
创建spring需要使用的配置文件
测试
maven依赖
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| <dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.2.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
|
接口和实现类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
public interface SomeService {
void doSome();
}
public class SomeServiceImpl implements SomeService {
public SomeServiceImpl() {
System.out.println("SomeServiceImpl类的无参构造执行了...");
}
@Override
public void doSome() {
System.out.println("执行了SomeServiceImpl的doSome()方法");
}
}
|
ioc配置文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="someService" class="com.mms.service.impl.SomeServiceImpl"/>
<bean id="someService2" class="com.mms.service.impl.SomeServiceImpl"/>
<bean id="myString" class="java.lang.String"/>
</beans>
|
测试程序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
|
@Test
public void test02() {
String config = "beans.xml";
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config);
SomeService service = (SomeService)ac.getBean("someService");
service.doSome();
}
@Test
public void test03() {
String config = "beans.xml";
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config);
}
@Test
public void test04() {
String config = "beans.xml";
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config);
int beansCount = ac.getBeanDefinitionCount();
System.out.println("spring容器中的对象个数="+beansCount);
String[] beansNames = ac.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String beanName : beansNames) {
System.out.println(beanName);
}
}
|
2.3.4 案例总结
spring配置文件中一个bean标签就代表一个对象,该对象有bean标签的id值唯一标识,从spring拿对象是使用getBean(“bean标签的id值”)
spring默认是使用类的无参构造来创建对象的
2.3.5 简单类型属性的赋值(set注入)
在入门案例的总结我们说过了spring容器默认是使用无参构造构造来实例化对象的,那么对象的属性必定为初始值,例如int类型为0,boolean类型为false等,那么当我们想使用相关属性进行操作时必然要手动使用set方法给属性赋值,那么有没有办法让容器帮我们完成对象属性的赋值呢?让我们直接就能够从容器中拿到有属性值的对象?答案是肯定的,下面就通过代码演示简单类型的属性赋值。
set注入要求
JavaBean必须要有set方法,因为ioc容器是使用javabean的set方法进行属性赋值的
spring容器调用的是setXxx()方法,而不管对象是否具有Xxx属性(即对象没有的属性只要有set方法也可以实现注入),Xxx不区分大小写
看看代码:
JavaBean
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private School school;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setSchool(School school) {
this.school = school;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", school=" + school +
'}';
}
}
|
spring配置文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| <!--声明Student对象-->
<bean id="student" class="com.mms.component.Student">
<!--
1、简单类型使用property和value标签给对象属性赋值
2、简单类型:8个基本类型+String
3、当spring容器加载到这一行时会在创建完对象的同时使用对象的set方法给属性赋值,底层
调用的是对象的set方法
4、spring容器调用的是setXxx()方法,而不管对象是否具有Xxx属性,Xxx不区分大小写
-->
<property name="name" value="张三"/>
<property name="age" value="23"/>
<!--测试对象没有属性的set方法-->
<property name="graName" value="s1"/>
</bean>
|
测试类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| //使用set注入给对象属性赋值
@Test
public void test01() {
String config = "ba01/applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config);
//执行完14行此时Student对象的属性已被赋值,获取对象进行验证
Student stu = (Student) ac.getBean("student");
System.out.println(stu); //Student{name='张三', age=23}
}
//验证set注入调用的是对象的set方法
@Test
public void test02() {
String config = "ba01/applicationContext.xml";
/*
* 此时会调用set方法进行赋值
* setName...
* setAge...
*/
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config);
}
//验证没有属性的setXxx方法是否报错
@Test
public void test03() {
String config = "ba01/applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config);
//获取对象
Student stu = (Student) ac.getBean("student");
}
|
2.3.6 非简单类型属性的赋值(set注入)
上文中的set注入使用property标签的name和value属性给对象属性赋值,但是value知识给简单类型属性赋值,对于非简单类型我们是使用property标签的name和ref属性给对象属性赋值。我们现在给Student类增加一个属性address,该属性是一个引用类型,那当ioc容器创建Student对象时如何给address属性赋值呢?
Student类:别的地方与上文的student类一致,这里只给出address属性和其set方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
private Address address;
public void setAddress(Address address) {
System.out.println("引用类型address的set方法执行了...");
this.address = address;
}
|
Address类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| public class Address {
private String homeAddress;
private String schoolAddress;
public void setHomeAddress(String homeAddress) {
this.homeAddress = homeAddress;
}
public void setSchoolAddress(String schoolAddress) {
this.schoolAddress = schoolAddress;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Address{" +
"homeAddress='" + homeAddress + '\'' +
", schoolAddress='" + schoolAddress + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
|
applicationContext.xml配置文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| <!--声明Student对象-->
<bean id="student" class="com.mms.component.Student">
<property name="name" value="张三"/>
<property name="age" value="23"/>
<!--测试对象没有属性的set方法-->
<property name="graName" value="s1"/>
<!--
引用类型属性的set注入
property标签属性
name:属性名
ref:引用对象的id值
-->
<property name="address" ref="address"/>
</bean>
<!--Student对象的引用属性Address-->
<bean id="address" class="com.mms.component.Address">
<!--set注入-->
<property name="homeAddress" value="新疆"/>
<property name="schoolAddress" value="西安"/>
</bean>
|
上文执行流程分析:当ioc容器创建id为student的对象时,会进行set注入,当执行到最后一个property标签时发现使用了ref属性,则ioc容器知道了name为address的属性是非简单类型,它就会暂时跳过address属性的赋值以及Student对象的创建,转而去配置文件的下文去找bean标签id值等于ref属性值的对象,现将该对象创建,再将该对象赋值给之前的address属性并将Student对象创建。
2.3.7 构造注入
顾名思义,构造注入是使用javabean的构造方法进行属性的赋值的。与set注入一样,构造注入要求javabean必须提供构造方法,且必须是有参构造(如果是无参构造还怎么给属性赋值,对吧),构造注入使用较少,了解就可以了,我们一般使用set注入。看看代码吧,将Student类的set方法注释,加入构造方法,别的地方不用改变,只需要改变spring配置文件即可(这里就可以看出ioc容器与程序的解耦合的好处了)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| <!--
构造注入
1、使用constructor-arg标签完成构造注入
2、构造注入方式一:根据形参名字
3、构造注入方式二:根据形参顺序,默认下标从0开始递增
-->
<!--根据形参名构造注入,形参的出现顺序不是必须的-->
<bean id="student" class="com.mms.value.Student">
<constructor-arg name="name" value="李四"/>
<constructor-arg name="age" value="24"/>
<constructor-arg name="address" ref="address"/>
</bean>
<bean id="address" class="com.mms.value.Address">
<constructor-arg name="homeAddress" value="新疆"/>
<constructor-arg name="schoolAddress" value="西安"/>
</bean>
<!--构造注入,使用下标,出现的顺序没要求,因为已经通过下标绑定起来了-->
<bean id="diByContructor" class="com.mms.value.Student">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="赵六"/>
<constructor-arg index="1" value="26"/>
<constructor-arg index="2" ref="address"/>
</bean>
|
2.3.8 非简单类型的自动注入
对于非简单类型,我们在上面是使用ref属性指向一个非简单类型的对象来完成赋值的,那么当ioc容器每次给一个对象的非简单类型属性赋值时,就要在bean标签内部写一行ref这样的代码,这样会造成重复代码的大量堆积,可以使用引用类型的自动注入。
有两种方式的引用类型自动注入
byName形式的引用类型自动注入:
通过java对象引用类型的属性名与spring容器中bean标签对象的id值一样且数据类型是一致的,这样能够实现引用类型的自动注入
byType形式的引用类型自动注入
通过java对象引用类型属性的数据类型和spring容器中 bean标签的class属性值是同源关系;
常见的同源关系:
1)java引用类型属性数据类型和bean标签的class属性值数据类型一样
2)java引用类型属性数据类型和bean标签的class属性值数据类型是父子关系
3)java引用类型属性数据类型和bean标签的class属性值数据类型是接口和实现类关系
注意:在一个配置文件中,符合条件的同源关系只能有一个
下面通过配置文件来详细说明两种形式的实现,在这里还是以Student类的address属性为例来说明。
byName形式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| <bean id="student" class="com.mms.ba03.Student" autowire="byName">
<!--简单类型赋值-->
<property name="name" value="张三"/>
<property name="age" value="23"/>
</bean>
<!--引用类型-->
<bean id="school" class="com.mms.ba03.School">
<property name="schoolName" value="石河子大学"/>
<property name="schoolAddress" value="石河子市"/>
</bean>
|
匹配详解: 当ioc容器在创建Student对象时,发现使用了autowire属性且属性值为byName,ioc容器就会去Student类中去拿引用类型的属性名与和spring配置文件中的bean标签的id值进行比对,若发现有一致的且数据类型一致,则将该对象赋值给引用类型属性。
byType形式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| <!--使用byType实现引用类型自动注入-->
<bean id="student2" class="com.mms.ba03.Student" autowire="byType">
<!--简单类型赋值-->
<property name="name" value="李四"/>
<property name="age" value="24"/>
</bean>
<!--引用类型
<bean id="school2" class="com.mms.ba03.School">
<property name="schoolName" value="西南大学"/>
<property name="schoolAddress" value="重庆市"/>
</bean>-->
<!--声明School的子类-->
<bean id="primarySchool" class="com.mms.ba03.PrimarySchool">
<property name="schoolName" value="西北大学"/>
<property name="schoolAddress" value="西安"/>
</bean>
|
2.4 基于注解的di实现
除了使用配置文件实现ioc创建对象的功能外,使用spring提供的注解也可以实现di。下面来介绍注解方式的di实现,下面是spring提供的di实现的常用注解。
@Component:该注解的功能是使用spring容器创建对象
1)、在要创建对象的类的声明上方加入该注解,该注解有一个属性value,value为spring创建的该类对象的id值
2)、开发中使用将value省略,直接使用双引号将值键入即可
3)、该注解使用类的无参构造创建对象
@Repository 创建dao类对象,访问数据库的对象
@Service 创建service类对象,业务层对象
@Controller 创建控制器对象,用于分发用户的请求和显示处理结果
下面通过代码来看看@Component注解是怎么实现di的。
1
2
3
4
| @Component(value = "student")
public class Student {
...
}
|
该语句就等价为在spring配置文件中进行了以下声明
1
| <bean id = "student" class = "com.mms.component.Student"/>
|
但是怎么让配置文件知道哪些类是使用注解进行创建对象的呢?需要在配置文件中声明组件扫描器
1
| <context:component-scan base-package="com.mms.component"/>
|
当spring读取配置文件时,读取到组件扫描器声明语句时,就会去base-package指定的包和其子包下去递归的寻找有注解修饰的类,并根据注解的功能去执行相应的动作
2.4.1 简单类型的注解di实现
简单类型的注入使用@Value注解实现,哪些简单类型要设置属性值,直接在简单类型属性声明语句的上面加入注解@Value即可,并在@Value的括号内键入属性值,注意不论简单类型属性的数据类型,均由双引号将属性值括起来。例如之前的Student类使用注解注入如下。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| @Component("student")
public class Student {
@Value("张三")
private String name;
@Value("23")
private int age;
}
|
注意别忘了该类要加注解@Component注解,因为要创建该类对象。
2.4.2 引用类型的注解di实现
引用类型的注入使用@Autowired注解完成。
@Autowired
@Autowired是spring提供的属性赋值,用于给引用类型赋值,有byName和byType两种方式,默认使用byType方式自动注入
若是要强制至于byName方式,要在@Autowired注解下面加入 @Qualifier(value = “bean的id”)注解,若程序在给引用类型注入时在xml文件中找不到 该id的bean标签或者手找不到该id的@Component注解,则报错;若不想让程序在赋值失败时报错,可以在@Autowired注解的required属性值置为false
还是拿Student类的school属性的赋值来举例。
学生类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| @Component("student")
public class Student {
@Autowired(required = false)
@Qualifier(value = "mySchool")
private School school;
}
|
School类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| @Component("mySchool")
public class School {
@Value("西南大学")
private String schoolAddress;
@Value("新疆")
private String homeAddress;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "School{" +
"schoolAddress='" + schoolAddress + '\'' +
", homeAddress='" + homeAddress + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
|
3、AOP
3.1 动态代理
3.1.1 jdk动态代理
使用jdk中的Proxy,Method,InvocaitonHanderl创建代理对象。 jdk动态代理要求目标类必须实现接口,关于细节本文就不赘述了。
要求:
必须要有接口
目标类必须实现接口(一个或多个)
3.1.2 cglib动态代理
第三方的工具库,创建代理对象,原理是继承。 通过继承目标类,创建子类。子类就是代理对象。 要求目标类不能是final的,方法也不能是final的
3.1.3 动态代理的好处
在目标类源代码不改变的情况下,增加功能。
减少代码的重复
专注业务逻辑代码
解耦合,让你的业务功能和日志,事务等非业务功能分离。
3.2 什么是AOP
面向切面编程, 基于动态代理的,可以使用jdk,cglib两种代理方式。Aop就是动态代理的规范化, 把动态代理的实现步骤,方式都定义好了, 让开发人员用一种统一的方式,使用动态代理实现。
3.2.1 AOP常用术语
Aspect: 切面,给你的目标类增加的功能,就是切面。 像日志,事务都是切面。切面的特点: 一般都是非业务方法,独立使用的。
JoinPoint:连接点 ,连接业务方法和切面的位置。需要给哪个方法增加切面,这个方法就是连接点。
Pointcut : 切入点 ,指多个连接点方法的集合。
目标对象: 给哪个类的方法增加功能, 这个类就是目标对象。
Advice:通知,通知表示切面功能执行的时间。
3.2.2 切面的构成
切面就是要给别的方法进行增强的方法,一个切面有以下三个要素。
切面的功能代码,切面干什么
切面的执行位置,使用Pointcut表示切面执行的位置
切面的执行时间,使用Advice表示时间,在目标方法之前,还是目标方法之后。
3.3 使用aspectJ框架实现AOP
3.3.1 aspectJ简介
aspectJ是一个开源的专门做aop的框架。spring框架中集成了aspectj框架,通过spring就能使用aspectj的功能。aspectJ框架实现aop有两种方式:
使用xml的配置文件 : 配置全局事务
使用注解,我们在项目中要做aop功能,一般都使用注解, aspectj有5个注解。
再使用aspectJ做aop之前要先加入aspectJ依赖。
1
2
3
4
5
6
| <!--aspectJ依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>5.2.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
|
3.3.2 @Before前置通知
前置通知注解修饰的切面在连接点方法之前执行。下面通过一段代码体验一下。
声明接口IService
1
2
3
| public interface IService {
void doSome(String name, int age);
}
|
声明实现类ServiceImpl
1
2
3
4
5
6
| public class ServiceImpl implements IService {
@Override
public void doSome(String name, int age) {
System.out.println("===doSome()===");
}
}
|
声明切面
切面类需要在顶部注解@Aspect 同时在xml文件中也要注册并加入<aop:aspect-autoproxy/>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| @Aspect
public class MyAspectJ {
@Before(value = "execution(* *..ServiceImpl.doSome(..))")
public void beforeLog(JoinPoint jp) {
System.out.println("连接点方法的方法签名="+jp.getSignature());
System.out.println("连接点方法的方法名="+jp.getSignature().getName());
Object[] args = jp.getArgs();
for (Object arg : args) {
System.out.println("arg="+arg);
}
}
}
|
测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| public class MyTest {
@Test
public void test01() {
String config = "ba01/applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config);
IService service = (IService) ac.getBean("service");
service.doSome("张三",23);
}
}
|
3.3.3 @AfterReturning后置通知
在IService接口中新增方法:
1
| Student doStudent(Student student);
|
在ServiceImpl实现doStudent方法
1
2
3
4
| @Override
public Student doStudent(Student student) {
return student;
}
|
切面类代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| @Aspect
public class MyAspectJ {
@AfterReturning(value = "execution(* *..ServiceImpl.doStudent(..))", returning = "obj")
public void afterTransaction(JoinPoint jp, Object obj) {
System.out.println(obj);
Student student = new Student();
student.setName("李四");
student.setAge(24);
obj = student;
System.out.println("===查看是否改变了连接点方法的返回值==="+obj);
}
}
|
3.3.4 @Around环绕通知(功能最强的通知)
环绕通知是功能最强的通知,它的本质就是jdk动态代理,他可以在连接点方法之前和之后都可以执行,最厉害的是他可以改变连接点方法的执行结果(返回结果)。还是拿上面的doStudent(Student student)方法来说明,经过验证前置通知和后置通知都不能改变doStudent(Student student)方法的返回值。下面看一下环绕通知是如何做的。
切面类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
| @Aspect
public class MyAspectJ {
@Around(value = "pointCut()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pj) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("环绕通知在连接点方法之前执行了...");
Object result = null;
result = pj.proceed();
Student student = new Student();
student.setName("李四");
student.setAge(24);
result = student;
System.out.println("事务已提交...");
return result;
}
@Pointcut(value = "execution(* *.doStudent(..))")
public void pointCut() {
}
}
|
4、整合mybatis
3.1 梳理整合思路
所谓的spring整合mybatis就是把两者集成在一起,就像使用一个框架一样。
mybatis框架开发步骤
定义mapper接口,定义方法
定义mapper.xml映射文件
创建mybatis核心配置文件
创建SqlSession对象,使用该对象生成mapper接口的代理对象执行方法
spring整合mybatis的核心就是把mybatis开发用到的对象交由spring容器ioc来创建,这样就做到了整合的目的。
在开发中,我们一般不使用mybatis自带的数据源,而是使用别的数据源,比如c3p0,dbcp等,本人使用的是阿里的druid数据源。
4.2 整合实现
4.2.1 环境搭建
导入相关依赖:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
| <dependencies>
<!--单元测试-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.11</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--spring核心ioc-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.2.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.2.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--mybatis依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.1</version>
</dependency>
<!--mybatis和spring集成的依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>1.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<!--mysql驱动-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9</version>
</dependency>
<!--阿里公司的数据库连接池-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.12</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<!--目的是把src/main/java目录中的xml文件包含到输出结果中。输出到classes目录中-->
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory><!--所在的目录-->
<includes><!--包括目录下的.properties,.xml 文件都会扫描到-->
<include>**
*.xml</include>
</includes>
<filtering>false</filtering>
</resource>
</resources>
<!--指定jdk的版本-->
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
|
重点是注意resources标签的配置,很多人都是在这里出错导致程序运行报错找不到mapper.xml文件
4.2.2 案例
本案例从student表中查询学生和新增学生功能。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| 实体类Student
public class Student {
private int stuNo;
private String stuName;
private int cardID;
private int classID;
public Student() {
}
public Student(int stuNo, String stuName, int cardID, int classID) {
this.stuNo = stuNo;
this.stuName = stuName;
this.cardID = cardID;
this.classID = classID;
}
public int getStuNo() {
return stuNo;
}
public void setStuNo(int stuNo) {
this.stuNo = stuNo;
}
public String getStuName() {
return stuName;
}
public void setStuName(String stuName) {
this.stuName = stuName;
}
public int getCardID() {
return cardID;
}
public void setCardID(int cardID) {
this.cardID = cardID;
}
public int getClassID() {
return classID;
}
public void setClassID(int classID) {
this.classID = classID;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"stuNo=" + stuNo +
", stuName='" + stuName + '\'' +
", cardID=" + cardID +
", classID=" + classID +
'}';
}
}
|
mapper接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
| public interface StudentMapper {
List<Student> queryAll();
void addStudent(Student student);
}
|
mapper.xml映射文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.mms.mapper.StudentMapper">
<!--查询全部-->
<select id="queryAll" resultType="Student">
select * from student
</select>
<!--新增学生-->
<insert id="addStudent" parameterType="Student">
insert into student (stuno,stuname,cardid,classid)
values (#{stuNo},#{stuName},#{cardID},#{classID})
</insert>
</mapper>
|
service接口
1
2
3
4
| public interface IStudentService {
List<Student> queryAll();
void addStudent(Student student);
}
|
service实现类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| public class StudentServiceImpl implements IStudentService {
private StudentMapper mapper;
public void setMapper(StudentMapper mapper) {
this.mapper = mapper;
}
@Override
public List<Student> queryAll() {
return mapper.queryAll();
}
@Override
public void addStudent(Student student) {
mapper.addStudent(student);
}
}
|
mybatis核心配置文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<typeAliases>
<!--
批量设置别名,会自动的将该包下的所有类定义了别名,别名就是其自身且不区分大小
-->
<package name="com.mms.entity" />
</typeAliases>
<!--加载映射配置文件-->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/mms/mapper/studentMapper.xml"></mapper>
</mappers>
</configuration>
|
在这里由于数据源对象我们是交由spring容器托管了,因此mybatsi核心配置文件中就没有environments标签了。
spring配置文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--加载数据库配置文件-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"/>
<!--声明数据源-->
<bean id="myDataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" init-method="init" destroy-method="close">
<!--set注入给数据库信息赋值,不需要指定驱动类,sprinf根据url自动识别
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true&serverTimezone=UTC"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="333"/>-->
<!--使用db配置文件读取数据库信息,格式类似el表达式-->
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</bean>
<!--声明的是mybatis中提供的SqlSessionFactoryBean类,这个类内部创建SqlSessionFactory的-->
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<!--set注入赋值-->
<!--set注入,把数据库连接池付给了dataSource属性-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="myDataSource" />
<!--mybatis主配置文件的位置
configLocation属性是Resource类型,读取配置文件
它的赋值,使用value,指定文件的路径,使用classpath:表示文件的位置
-->
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis-config.xml" />
</bean>
<!--创建dao对象,使用SqlSession的getMapper(StudentDao.class)
MapperScannerConfigurer:在内部调用getMapper()生成每个dao接口的代理对象。
-->
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<!--指定SqlSessionFactory对象的id-->
<property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="sqlSessionFactory" />
<!--指定包名, 包名是dao接口所在的包名。
MapperScannerConfigurer会扫描这个包中的所有接口,把每个接口都执行
一次getMapper()方法,得到每个接口的dao对象。
创建好的dao对象放入到spring的容器中的。 dao对象的默认名称是 接口名首字母小写
-->
<property name="basePackage" value="com.mms.mapper"/>
</bean>
<!--声明service-->
<bean id="studentServiceImpl" class="com.mms.service.impl.StudentServiceImpl">
<property name="mapper" ref="studentMapper"/>
</bean>
</beans>
|
数据库配置文件
1
2
3
| url = jdbc:mysql:
username = Xxx
password = Xxx
|
测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
@Test
public void test02() {
String config = "applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config);
StudentMapper mapper = (StudentMapper) ac.getBean("studentMapper");
List<Student> students = mapper.queryAll();
for (Student student : students) {
System.out.println("student--->"+student);
}
}
@Test
public void test03() {
String config = "applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config);
IStudentService service = (IStudentService) ac.getBean("studentServiceImpl");
Student student = new Student();
student.setStuName("呵呵");
student.setStuNo(1111);
student.setCardID(1115);
student.setClassID(1);
service.addStudent(student);
}
|
5、处理事务
5.1 什么是事务
事务是指一组sql语句的集合, 集合中有多条sql语句可能是insert , update ,select ,delete, 我们希望这些多个sql语句都能成功,或者都失败, 这些sql语句的执行是一致的,作为一个整体执行。关于事务最经典的例子就是转账了。
5.2 使用spring内部注解处理事务
加入事务相关依赖
1
2
3
4
5
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>5.2.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
|
案例:数据库有两张表,一张sale表,该表是商品订单信息;一张goods表,该表是商品库存信息。service类有一个业务方法buy,该方法指定要购买商品的id和数量,dao有三个方法分别是像sale表增加一条购买记录、更新goods表的库存信息、在goods表查询指定id商品是否存在。
下面是两张表的记录信息
sale表(初始是空表,因为还没有购买记录),id字段自增长
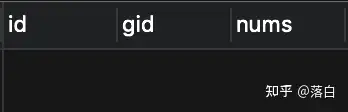
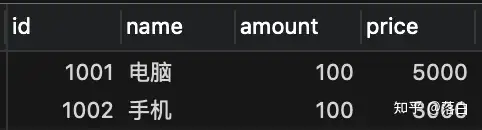
goods表
业务流程大致是这样,用户向buy方法传递两个参数,分别是goods表的id字段和购买数量nums。buy方法体中的第一个方法是向sale表增加一条记录,类似与buy(1002,20),那么sale表应该多出来一条如下记录
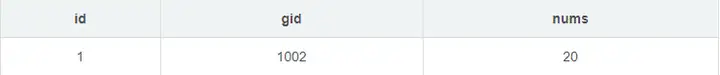
因为sale表id字段是自增长的,所以自动为1。
先看一下buy方法的定义
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| public void buy(Integer goodsId, Integer nums) {
Goods goods = goodsMapper.queryGoods(goodsId);
if (goods == null) {
} else if (goods.getAmount() < nums) {
}
}
|
首先根据用户传入的参数id和nums向sale表新增一条购买记录。即有商品卖出去了,那么我们理应更新一下库存对吧,不然怎么知道还有多少货,万一别人要买100件商品而你只有50件肯定会导致别人购买失败对吧。那么问题就就来了,当我们执行完向sale表新增记录后,就该更新库存了,我们必须要知道刚卖出去的商品是谁对吧,这个通过用户传入的id和商品表goods的id字段一一对应,所以先去数据库查询用户传入的id是否存在goods表中,若不存在应该将事务回滚,即前面向sale表增加的记录是不应该存在的;同理,若用户传入的id商品在goods表中,但是用户要求的数量大于该商品当前库存,事务也应该回滚;只有当用户传入的id商品和数量都满足条件时我们才应该更新库存并且提交事务。
该介绍的都介绍完了,开始着手干吧。
实体类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
| public class Goods {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer amount;
private Float price;
public Goods() {
}
public Goods(Integer id, String name, Integer amount, Float price) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.amount = amount;
this.price = price;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAmount() {
return amount;
}
public void setAmount(Integer amount) {
this.amount = amount;
}
public Float getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(Float price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Goods{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", amount=" + amount +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}
public class Sale {
private Integer id;
private Integer gid;
private Integer nums;
public Sale() {
}
public Sale(Integer id, Integer gid, Integer nums) {
this.id = id;
this.gid = gid;
this.nums = nums;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Integer getGid() {
return gid;
}
public void setGid(Integer gid) {
this.gid = gid;
}
public Integer getNums() {
return nums;
}
public void setNums(Integer nums) {
this.nums = nums;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Sale{" +
"id=" + id +
", gid=" + gid +
", nums=" + nums +
'}';
}
}
|
mapper接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| public interface GoodsMapper {
void updateGoods(Goods goods);
Goods queryGoods(Integer id);
}
public interface SaleMapper {
void addSale(Sale sale);
}
|
mapper.xml映射文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| <mapper namespace="com.mms.mapper.GoodsMapper">
<!--更新商品信息-->
<update id="updateGoods" parameterType="Goods">
update goods set amount = amount - #{amount} where id = #{id}
</update>
<!--查询商品信息-->
<select id="queryGoods" resultType="Goods">
select * from goods where id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>
<mapper namespace="com.mms.mapper.SaleMapper">
<!--增加销售记录-->
<insert id="addSale" parameterType="Sale">
insert into sale (gid,nums) values (#{gid},#{nums})
</insert>
</mapper>
|
service接口
1
2
3
4
| public interface IBuyGoodsService {
void buy(Integer goodsId,Integer nums);
}
|
service实现类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
| public class BuyGoodsServiceImpl implements IBuyGoodsService {
private SaleMapper saleMapper;
private GoodsMapper goodsMapper;
public void setSaleMapper(SaleMapper saleMapper) {
this.saleMapper = saleMapper;
}
public void setGoodsMapper(GoodsMapper goodsMapper) {
this.goodsMapper = goodsMapper;
}
@Transactional
@Override
public void buy(Integer goodsId, Integer nums) {
System.out.println("buy开始...");
Sale sale = new Sale();
sale.setGid(goodsId);
sale.setNums(nums);
saleMapper.addSale(sale);
Goods goods = goodsMapper.queryGoods(goodsId);
if (goods == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("编号为:"+goodsId+"商品不存在...");
} else if (goods.getAmount() < nums) {
throw new NotEnoughException("编号为:"+goodsId+"商品库存不足...");
}
Goods good = new Goods();
good.setId(goodsId);
good.setAmount(nums);
goodsMapper.updateGoods(good);
System.out.println("buy结束...");
}
}
|
mybatis核心配置文件和整合mybatis一致,这里就不给出了
spring配置文件也和整合部分一致,只需要在根标签beans加入以下部分即可
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| <!--声明使用spring的事务处理-->
<!--1、声明事务管理器-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<!--连接的数据库,指定数据源-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="myDataSource"/>
</bean>
<!--2、开启事务注解驱动,告诉sprint使用注解管理事务,创建代理对象-->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
|
测试类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
@Test
public void test01() {
String config = "applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config);
IBuyGoodsService service = (IBuyGoodsService) ac.getBean("buyGoodsService");
service.buy(1002,10);
}
|
5.3 使用aspectj框架处理事务
aspectJ处理事务是基于配置文件形式的,别的地方都和上面一样,只需要更改service实现类的buy方法和spring核心配置文件即可。
1、取消buy方法上的事务注解,因为我们现在是使用aspectJ,基于配置文件
2、将spring注解形式事务开发的spring配置文件中加入的声明事务管理器的部分换成下面的配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| <!--
使用aspectj方式的事务(声明式事务)
1、aspectj事务适合大型项目,因为其声明在配置文件中,大大与程序解耦合
-->
<!--1、声明事务管理器-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="myDataSource"/>
</bean>
<!--
2、声明业务方法的事务属性(隔离级别、传播行为、超时时间)
id:自定义
transaction-manager:事务故管理器对象的id值
-->
<tx:advice id="myAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<!--tx:attributes配置事务属性-->
<tx:attributes>
<!--
tx:method:给具体的方法配置事务属性,method可以有多个,由于给多个方法配置事务
name:方法名,不带包名和类名,方法可以使用通配符
propagation:传播行为,枚举类
isolation:隔离级别
rollback-for:你指定的异常全限定类名,发生异常一定回滚
-->
<tx:method name="buy"
propagation="REQUIRED"
isolation="DEFAULT"
rollback-for="java.lang.NullPointerException,com.mms.exception.NotEnoughException"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<aop:config>
<!--
3、配置切入点表达式
为什么需要配置切入点表达式?
因为步骤2中的方法不确定是哪一个类、哪一个包的方法,所以需要指定
-->
<aop:pointcut id="servicePt" expression="execution(* *..service..*.*(..))"/>
<!--
配置增强器,用于关联advice和pointcut
advice-ref:通知,上面的tx:advice的id值
pointcut-ref:切入点表达式的id值
-->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="myAdvice" pointcut-ref="servicePt"/>
</aop:config>
|
测试类与前面的一样。



